Student learning outcomes is a very common term in education. For many of my k-12 colleagues we have used this term from graduate course work, to teaching practicum, and for curriculum planning. The challenge in writing student learning outcomes happens when you have to find actionable items and SPECIFIC methods for learning assessment.
Last week I attended “Writing student learning outcomes and the GSTEP teaching template: How they inform your teaching” for the G*STEP program presented by Shana Cole & Nancy Fire from CLEAR.
We talked about components of a teaching strategy, which included:
A. Context for your teaching strategy
B. Selecting learning challenges to address with your teaching strategy
C. Objectives for this experience
D. Foundational knowledge necessary for students to participate in teaching strategy
E. Step by step planning
F. Ground rules (if needed for you strategy)
G. Assessment: How do you plan to assess the effectiveness of your learning strategy?
H. Anticipated Challenges: Indicate how you plan to deal with any of these challenges that may apply. Describe.
I. Journal Reflection
The three level model for student learning outcome development, which included the following levels:
- Goal
- General Learning Outcomes (GLOs)
- Specific Learning Outcomes (SLOs)
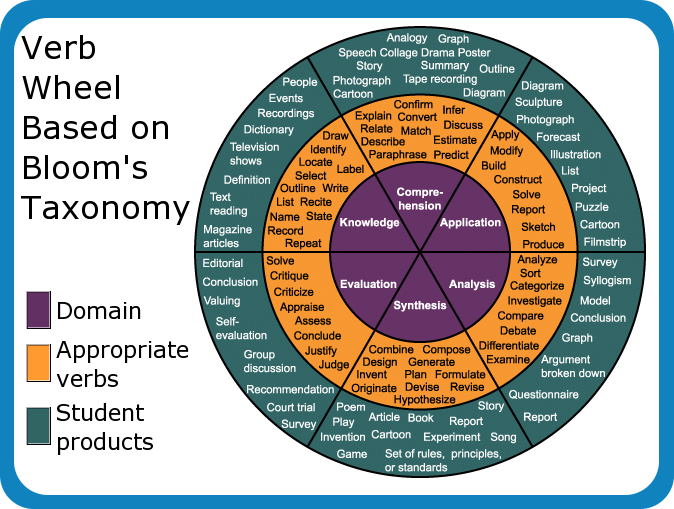
The last step – Specific Learning Outcomes (SLOs) – is where we focused our attention. Specific learning outcomes are highly measurable and possess detailed requirements. As an instructional designer who is often involved in program evaluation or course design, I appreciated the cross-disciplinary conversations on how to meet various subject matter content issues with the needs of the learner. A helpful resource to keep us on the same page and to guide our SLOs discussion was the Bloom’s Taxonomy verb wheel. This was a practical tool that helped to focus our planning and here were some of the key points I gleaned from the overall workshop:
- be clear, specific & measurable
- identify what the students should be able to do as a result of a learning experience
- display evidence that learning has occurred at a specified competency level
- focus shifts from what “I will teach” to “what students will learn”
- define content, expectations, assessments & creates constructive data i.e. data, percentage, and understanding of student learning
For student learning outcomes to work they have to connect to the learning. A great way to assess your expectations of your SLOs is to share these with other educators, both inside and outside your discipline or subject matter expertise. Student learning outcomes need to be written at a general level to ensure clear communication, and limit subjective language. By using SLOs you are able to modify course objectives, assess curriculum design, and measure how your instruction impacts learners. By creating 3-7 overall goals in your course, you will want to consider at least 3-5 specific learning outcomes to measure each goal. These goals will help address your teaching strategy and how you assess your learner’s progress.
How do your specific learning outcomes (SLOs) fit into your entire course planning and content delivery?




You must be logged in to post a comment.