Beginning with the end in mind. This is the philosophy of instructional design method backward(s) design. A few weeks back Kevin Guidry shared his thoughts on backward design, and it got me thinking about how I approach my curriculum and lesson plans.

Image c/o <http://www.recordholders.org/images/backwards-cycling1.jpg>
For the Office for Exploring Majors, I am currently reviewing/updating modules for our first-year seminar class – UGST 1000. The goal is to offer an “engaged” format (we cannot use the term blended or hybrid, but there will be mixed components of online, in-class and active requirements) for Fall 2012. Last semester our department offered a couple of sections of the NextGen course; however, the class focus was on “well-being.” Since our office t works with undecided students, the engaged sections for Fall 2012 will need to be directed towards major/career exploration and academic success.
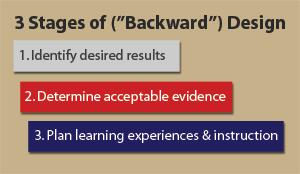
Image c/o <http://kids.esc13.net/curriculum/3stages.gif>
In reviewing the current curriculum, it was apparent that a backward design approach would be the most effective method for this instructional design project. In Understanding by Design, Wiggins and McTighe (2005) identify three key stages for backward design:
- Identify desired results (learning outcomes) – What should your learners know, understand, and be able to do?
- Determine Acceptable Evidence (means to assess if learners have learned) – How will you know if learners have achieved the desired results, achieved those learning outcomes, or met the standards? What is the evidence of learner understanding and proficiency?
- Plan learning experiences and instruction – What will be the procedures or methods to reach these outcomes? This includes a definition of knowledge; definition of skills and procedures learners need to master; definition of materials; and definition of learning or instructional activities.
Here is an example of an engaged learning module that I will include for the Time Management unit. This session will have the backward design steps and one of three classes that students will be required to complete outside of the in-class meeting time.
1. Learning Outcome(s)
Learners will be able to:
(a) identify the differences between tasks, objectives, and goals.
(b) create a smart and effective to-do list of tasks.
(b) assess their weekly schedule to identify how time is being utilized.
(c) select priorities, understand where time is lost, and accurately adjust for effective time management.
2. Evidence of Learning
Learners will demonstrate their understanding of learning by:
(a) drafting a to-do list of tasks for the day/week and identify 5 top priorities.
(b) mapping out a one week schedule of their activities to identify where their 168 hours are allocated.
(c) creating a visual representation of how the 1 week period time is accounted for in terms of activities and responsibilities.
(d) writing a 250 word minimum blog post/online journal about their 168 hours and weekly schedule. This reflection will include the visual representation of 168 hours, account for time wasted, and offer ideas how to effectively manage time to balance their schedule.
3. Learning Experiences & Instruction
This section of the time management unit will be housed online. We have some modules created on Blackboard Learn; however, I thought I would also create a mock up on the new TED-Ed website. This is a rough draft of a module (to be edited) I designed by “flipping the video” from YouTube into a lesson. [Side note: there are already a number of lessons available for educators to use for the experience section of lessons. Instructors can use the same module or “flip” it.]
TED-Ed | Time Management: How to Write a To-Do List & Know Where Your Time Goes
College Success – Chapter 2: 2.3 Organizing Your Time
References:
Beiderwell, B., Tse, L., Lochhaas, T.J., & deKanter, N.B. (2010, August). College success. Flatworld Knowledge. Retrieved from http://catalog.flatworldknowledge.com/catalog/editions/54
Wiggins, G. & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by design (2nd ed). NJ: Prentice Hall.





You must be logged in to post a comment.